LEVELS AND DISTRIBUTION OF POLYCHLORINATED BIPHENYLS IN THE ATMOSPHERE NEAR THE CHINESE GREAT WALL STATION, ANTARCTICA
Li YM 1, 2, Geng DW 1, Wang P 1, Zhang H 1, Jiang GB 1
1 State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, P.O. Box 2871, Beijing 100085, China 2 MTM Research Center, School of Science and Technology, Orebro University, Sweden
Introduction
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) have aroused great concern due to their adverse effect to the environment and human health. POPs are highly toxic, persistent and can bioaccumulate in fat tissues via food webs. Atmospheric transport plays a key role in the transportation of POPs from source regions, urban areas to rural, remote and polar regions. The Antarctica is considered to be a clean and pristine area due to less anthropogenic activities. However, more and more studies have reported the detection of various POPs in the Antarctic environment, including atmosphere, moss, fish species and marine mammals. In this study, both high volume air samplers and PUF-disk based passive air samplers were employed in the vicinity of the Chinese Great Wall Station on the King George Island, Antarctica, in the austral summer between December 2009 and February 2010. The main aim was to investigate the current contamination levels, distributions and potential sources of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in the atmosphere of the remote Antarctica islands.
Materials and Methods
For air monitoring program, two high volume (active) air samplers (AAS) and five PUF-disk passive air samplers (PAS) were located in the King George Island, Antarctica. The sampling site of the high volume sampling was 300m in the southwest of Chinese Antarctic Research Station (Great Wall Station, 62o13S', 58o 58'W). Sampling time was from December 11th, 2009 to February 5th, 2010, during the 26th Chinese Antarctic Expedition. Fourteen high volume air samples were obtained with sampling volumes of —2000 m3 over each seven days period.
Sample extraction, cleanup and chemical analysis followed our previously established method 1,2. Briefly, 1 ng of 13C12-labeled surrogate standards of PCBs (Wellington Laboratories, Canada)) were spiked into the samples before an ASE extraction with organic solvents (hexane: dichloromethane=1:1). The extracts were concentrated and followed by a cleanup with acid silica gel and multilayer silica columns. The final extract was spiked with 1 ng 13C12-labeled injection standards of PCBs for recovery quantification prior to the injection into a high resolution gas chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry (HRGC/HRMS) equipped with a 60 m DB-5MS column.
Results and Discussion
Air Concentrations of PCBs
The air concentrations of 6 PCBs (CB-28, 52, 138, 153, 180) and total PCBs (∑206 PCBs) were reported. The total PCBs exclude three mono-PCB congeners due to low sample recoveries. The concentrations of ∑6 PCBs and total PCBs were in the range of 1.8-3.4 pg m-3 and 82-167 pg m-3, respectively. The air concentrations of total PCBs (∑206 PCBs) in the Korean Antarctica Stations, which is —10 km from the Great Wall Station, were reported in the range of 0.18-0.91 pg m-3 and 45-118 pg m-3, respectively, derived from XAD passive air sampling in 2005-2006 3. This result is consistent with the measurements in this study. The PCBs in the atmosphere of King George Island in the austral summer of 1995-1996 were reported as < 4.6-3.3 pg m-3 (CB-52), < 4.0-12 pg m-3 (CB-153) and < 2.3-10.4 pg m-3 (CB-153) 4, respectively, which is higher than the PCBs concentrations in our results.
The air samples were dominated by light homologues. Di-PCBs, Tri-PCBs and Tetra-PCBs were the dominate contributor to the total PCBs concentrations, which was responsible for an average contribution of 12%, 7.2% and 80%, respectively. However, the heavy PCBs account for very small contributions. This result is consistent with the results from the Korean Antarctic station and can be explained by the long range transportation and global cold trap effect 5.
Comparison between AAS and PAS Data
Figure 1 compares the PCBs concentrations from AAS and PAS. Figure 2 shows the PCBs distribution in the atmosphere of each PAS sampling site. The PAS derived air concentrations were calculated by using a daily sampling volume of 3.5 m-3 d-1. There was a 1-3 folds deviation of PCB concentrations between the active and passive sampling data. Therefore, PUF-disk passive air sampling can be used to assess PCBs distributions in the atmosphere of the Antarctica, although the wind speed are always high during the sampling campaigns. The three sampling sites, which are close to several Antarctic Stations, showed higher PCB concentrations than the other two sites. This result may reflect potential influences of PCBs contamination from human activities.
Figure 2 Concentrations of total PCBs in various PAS sampling site
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Chinese Arctic and Antarctic Ministration.
References
1. Li YM, Zhang QH, Ji DS, Wang T, Wang YW, Wang P, Ding L, Jiang GB. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2009, 43(4):1030-1035.
2. Wang P, Zhang QH, Wang YW, Wang T, Li XM, Ding L, Jiang GB. Analytica Chimica Acta. 2010, 663: 43-48.
3. Choi SD, Baek SY, Chang YS, Wania F, Ikonomou MG, Yoon YJ, Park BK, Hong S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008; 42: 7125.
4. Montone RC, Taniguchi S, Weber RR. Sci. Total. Environ. 2003; 308: 167.
5. Wania F, Mackay D. Global fractionation and cold condensation of low volatility organochlorine compounds in polar regions. Ambio, 1993; 22: 10.
Environmental Analysis Reference Standards available from Greyhound Chromatography, supplied by Wellington Laboratories, Chem Service Ins, Merck, High Purity Standards
Wellington Reporter May 2019
Wellington Reporter Discontinued Products | Greyhound Chromatography
PRODUCT DISCONTINUED
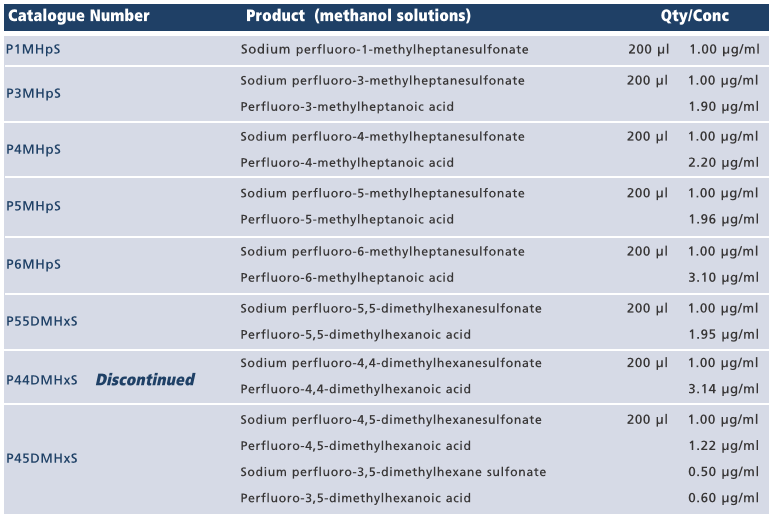
P44DMHxS
Unfortunately, P44DMHxS (a mixture of perfluoro-4-4-dimethylhexane sulfonate and perfluoro-4-4-dimethylhexanoic acid) is being discontinued due to limited interest and a lack of inventory. However, these compounds are identified as minor components in our br-PFOSK/T-PFOS and T-PFOA reference standards respectively. We apologize for any inconvenience this may cause and appreciate your understanding.
About Wellington Laboratories
For Over 35 years Wellington Laboratories Inc. has been internationally recognised as a trusted source of high quality reference standard solutions for use in environmental/analytical testing and toxicological research. Wellington Laboratories offers an extensive inventory of individual certified reference standards and solution mixtures of native and mass-labelled halogenated organic compounds including polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorinated dibenzofurans, polychlorinated biphenyls, halogenated flame retardants and perfluorinated compounds. Wellington Laboratories also offer a variety of calibration sets and support solutions designed to be used for common regulatory methods or modified in-house methods.
Wellington’s Reference Standards are used mainly in Environmental/analytical testing and toxicological research. Wellington offers an extensive inventory of individual certified reference standards and solution mixtures of native and mass-labelled halogenated organic compounds including polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorinated dibenzofurans, polychlorinated biphenyls, halogenated flame retardants and perfluoronated compounds. Wellington also offer a variety of calibration sets and support solutions designed to be used for common regulatory methods of modified in-house methods.
Wellington Laboratories are committed to the distribution of quality products as well as the maintenance of excellent customer service. In fact, in order to provide your customers with the best possible service, Wellington have three ISO certifications (ISO 9001:2008, ISO/IEC 17025:2005, and ISO Guide 34:2009) which cover all aspects of planning, production, testing, distribution, and post-distribution service. These certifications allow Wellington Laboratories to monitor and maintain the highest level of quality and service and also allow their customers to satisfy the requirements of their own ISO certifications.
Wellington’s ISO/IEC 17025:2005 accreditation has been certified by the Canadian Association for Laboratory Accreditation Inc. (CALA) the scope is available for review on the CALA Directory of Accredited Laboratories (http://www.cala.ca).
Similarly, Wellington’s ISO Guide 34:2009 accreditation has been certified by ANSI-ASQ National Accreditation Board (ANAB), the certificate and scope are available on their website (http://anab.org/).
We are able to supply hard copies of any of the ISO certificates for yourself and your customers.
Full Range of Wellington Laboratories' Products
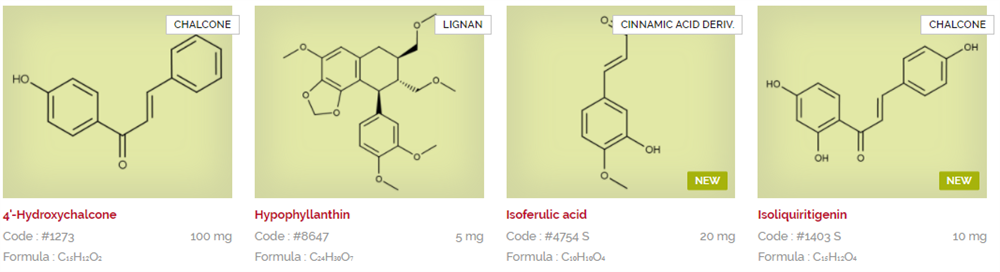
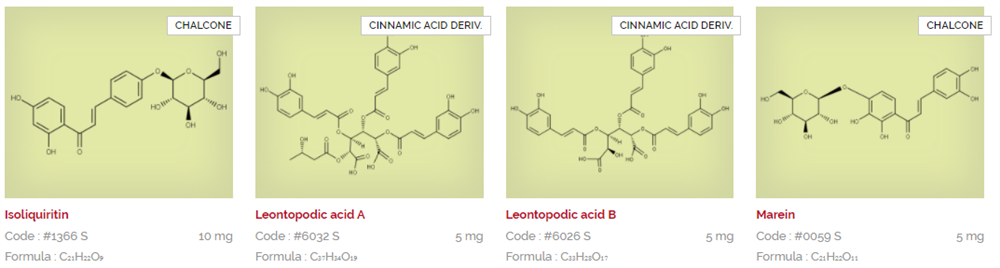
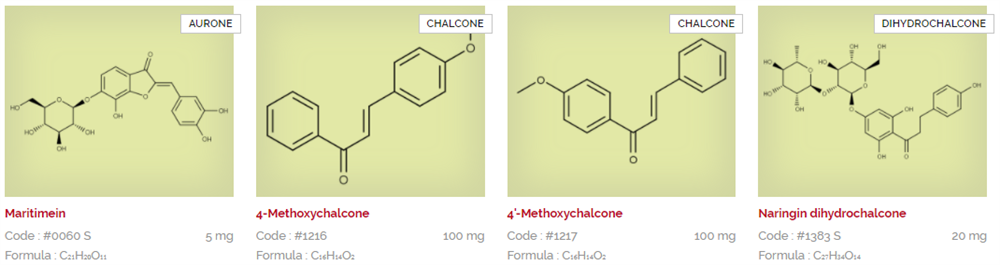
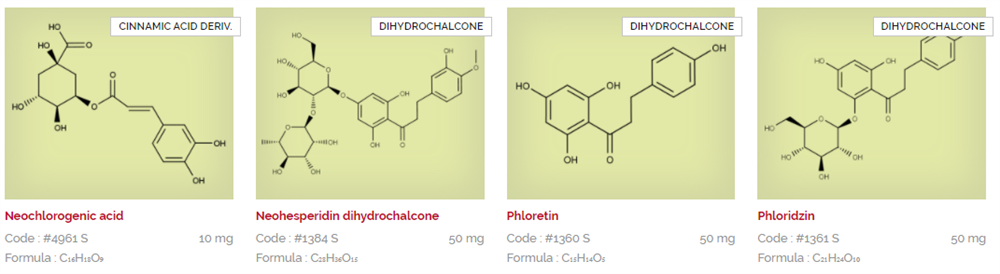
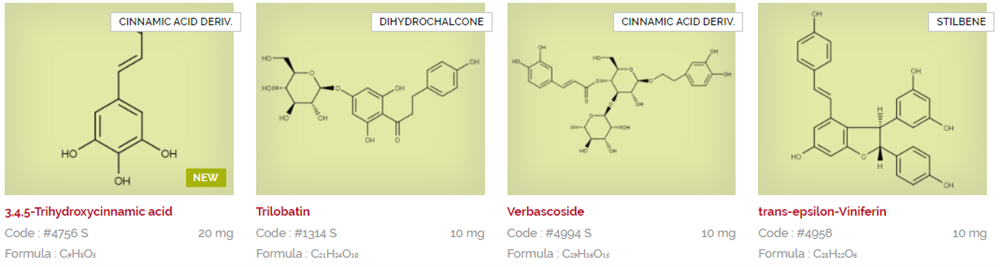
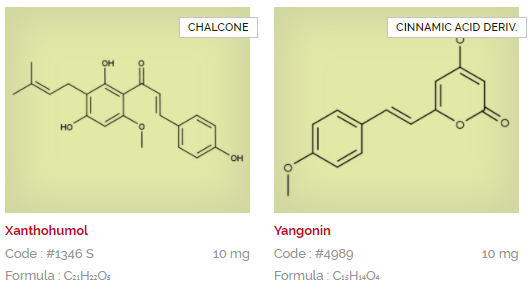
Extrasynthese are experts in extraction, synthesis and purification of natural substances. Their product portfolio consists of hundreds of products, after almost 30 years of research and development creating reference standards for regulatory filing, quality testing, or as substrates for early stage R&D. Download and view the Extrasynthese catalogues below listed in alphabetical order, or search via CAS or product name using the search facility.
    |
CONTACT US
Tel: +44 (0) 151 649 4000
Email: marketing@greyhoundchrom.com
FOLLOW US
YOU MAY ALSO BE INTERESTED IN OUR NEWSLETTER